Common names from other countries
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
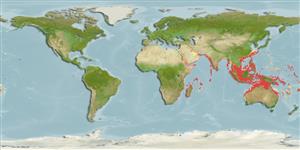
Marine; brackish; reef-associated; amphidromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 0 - 150 m (Ref. 5222). Tropical; 30°N - 32°S, 29°E - 173°W (Ref. 5222)
Indo-Pacific: Red Sea and East Africa to Tonga, north to Japan, south to Australia. It is not known from the Persian Gulf, where the closely related Epinephelus coioides is common.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 64.0 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 234 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5213); common length : 100.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5213); max. published weight: 150.0 kg (Ref. 9710)
Dorsal spines (total): 11; Dorsal soft rays (total): 14 - 16; Anal spines: 3; Anal soft rays: 8. Characterized by light grey to yellowish brown color; five slightly oblique dark brown bars that bifurcate ventrally; numerous small black spots and blotches in head and body; ctenoid scales on body except cycloid anterodorsally on body, thorax and abdomen; body with auxiliary scales; greatest depth of body 3.0-3.6 in SL; rounded caudal fin; pelvic fins, 2.0-2.6 in head length (Ref. 90102); head length 2.3-2.6 times in SL; snout length 1.7-2.0 times in upper jaw length; interorbital width 4.5-6.5 times in HL and 2.1-3.0 times in upper jaw length; flat or slightly convex interorbital area; subangular preopercle, with enlarged serrae at the angle; almost straight upper edge of operculum; subequal posterior and anterior nostrils, except in large adults which have the posterior nostrils slightly larger; maxilla reaches to or past vertical at rear edge of orbit, maxilla width 4.5-6.5% of SL; upper jaw length 17-22% of SL, 2-5 rows of teeth on midlateral part of lower jaw (Ref. 89707).
A common species found in a variety of habitats: coral and rocky reefs, tide pools, estuaries, mangrove swamps and sandy or mud bottom from shore to depths of 150 m. Solitary (Ref 90102). Juveniles found near shore and in estuaries; sex reversal probable; catch statistics poor being previously confused with E. andersoni (Ref. 4332). Feed primarily on fishes and crustaceans, and occasionally on cephalopods (Ref. 9710). Present in Hong Kong live fish markets (Ref. 27253). Widely used in mariculture mainly in the Far East (Ref. 43448).
Heemstra, P.C. and J.E. Randall, 1993. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 16. Groupers of the world (family Serranidae, subfamily Epinephelinae). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the grouper, rockcod, hind, coral grouper and lyretail species known to date. Rome: FAO. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(16):382 p. (Ref. 5222)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
CITES (Ref. 128078)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; aquaculture: commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
115969): 24.3 - 29.1, mean 28 (based on 2428 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01230 (0.00808 - 0.01874), b=3.05 (2.93 - 3.17), in cm Total Length, based on LWR estimates for this species & Genus-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 4.2 ±0.50 se; based on food items.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (Fec = 51,087).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate vulnerability (40 of 100).