Common names from other countries
Teleostei (teleosts) >
Anguilliformes (Eels and morays) >
Muraenidae (Moray eels) > Muraeninae
Etymology: Gymnothorax: Greek, gymnos = naked + Greek, thorax, -akos = breast (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Bleeker.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
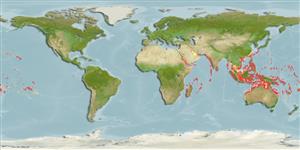
Marine; reef-associated; depth range 0 - 50 m (Ref. 30573). Tropical; 30°N - 25°S
Indo-Pacific: Red Sea and East Africa (Ref. 33390) to the Marquesas and Oeno Atoll (Pitcairn Group), north to the Ryukyu and Hawaiian islands, south to New Caledonia and the Austral Islands.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 300 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9710); max. published weight: 30.0 kg (Ref. 30404)
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Anal spines: 0; Vertebrae: 137 - 143. Juveniles are tan with numerous large black spots. Adults have black specks that grade into leopard-like spots behind the head and a black area surrounding the gill opening.
Found in lagoon and seaward reefs. Commonly seen species along deep drop-offs and slopes in Indonesian waters (Ref. 48635). Benthic (Ref. 58302). Juveniles more secretive and occur on intertidal reef flats (Ref. 37816). It feeds primarily on fishes and occasionally on crustaceans. This is the largest Indo-Pacific moray eel (Ref. 30404), perhaps reaching 3 m in length. Because of its position at the top of the reef's food chain it is often ciguatoxic. Attacks humans when provoked (Ref. 3132). Minimum depth reported taken from Ref. 10713. Solitary in reef holes (Ref 90102).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturities | Reproduction | Spawnings | Egg(s) | Fecundities | Larvae
Observations on prespawning behavior include a pair entwined around one another lying on the bottom of the reef area (Ref. 93344).
Chen, H.-M., K.-T. Shao and C.T. Chen, 1994. A review of the muraenid eels (Family Muraenidae) from Taiwan with descriptions of twelve new records. Zool. Stud. 33(1):44-64. (Ref. 6934)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
CITES (Ref. 128078)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 4690)
Human uses
Fisheries: subsistence fisheries; aquarium: public aquariums
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
115969): 25.5 - 29, mean 28.1 (based on 902 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00052 (0.00033 - 0.00084), b=3.27 (3.14 - 3.40), in cm Total Length, based on LWR estimates for this species & Genus-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.9 ±0.64 se; based on food items.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): High, minimum population doubling time less than 15 months (Fec = 200,000-300,000).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Very high vulnerability (90 of 100).