Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays) >
Carcharhiniformes (Ground sharks) >
Carcharhinidae (Requiem sharks)
Etymology: Carcharhinus: karcharos (Gr.), sharp or jagged; rhinus, an ancient name for sharks, from rhine (Gr.), rasp, both words alluding to a shark's jagged, rasp-like skin. (See ETYFish); humani: In honor of the late Brett A. Human (d. 2011), Australian marine biologist, Western Australian Museum (Perth), for “important contributions to shark taxonomy in South Africa and Oman in the western Indian Ocean region, and who is sorely missed by his colleagues”. (See ETYFish).
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
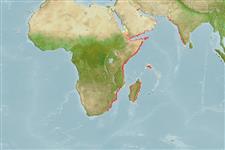
Marine; pelagic-neritic; depth range 36 - 43 m (Ref. 96342). Tropical
Western Indian Ocean: from Kuwait in the Persian (Arabian) Gulf, to Socotra Islands; south to Mozambique (Maputo Bay) and South Africa (Natal).
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 84.4 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 96342)
Short description
Identification keys | Morphology | Morphometrics
This species is distinguished by the following characters: moderately long and narrowly rounded snout; upper anterior teeth are oblique and blade-like, coarsely serrated, the lateral margin deeply notched and with several large, smooth basal cusplets; lower anterior teeth are narrower, slightly oblique, lateral margins notched and usually several smooth basal cusplets; total tooth row counts 24-26/22-25, or 46-50; a weak ridge usually present on midline of interdorsal space, 20.4-22.0% TL; moderately tall and slightly falcate first dorsal fin, its origin just anterior to pectoral-fin free rear tip, length 13.4-14.6% TL, 1.3-1.5 times height, inner margin 1.7-2.3 times in base; broadly triangular second dorsal fin, its height 39-48% of first dorsal-fin height, origin about opposite to anal-fin origin; anal fin falcate, height 0.8-1.0 times second dorsal height, base 0.9-1.2 times second dorsal-fin base; colour pale brownish to grey dorsally, whitish ventrally; second dorsal fin with a black blotch on upper one to two thirds of fin, not extending onto upper surface of body and strongly demarcated from ground colour; most other fins have whitish outer margins; total vertebral counts 153-160 in 4 type specimens (Ref. 6184:152-167); precaudal counts 75-79 (Ref. 6184:74-85); precaudal counts - monospondylous 45-48, diplospondylous 27-32; diplospondylous caudal counts 78-81 (Ref. 96342).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturities | Reproduction | Spawnings | Egg(s) | Fecundities | Larvae
White, W. and S. Weigmann, 2014. Carcharhinus humani sp. nov., a new whale shark (Carcharhiniformes: Carcharhinidae) from the western Indian Ocean. Zootaxa 3821(1):071-087. (Ref. 96342)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 24.1 - 28.3, mean 26 °C (based on 13 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01000 (0.00244 - 0.04107), b=3.04 (2.81 - 3.27), in cm total length, based on all LWR estimates for this body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 4.0 ±0.6 se; based on size and trophs of closest relatives
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (Preliminary low fecundity).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate to high vulnerability (54 of 100).